高级技巧:利用Lua编写安全场景的测试数据生成工具
2023-08-11阅读:291
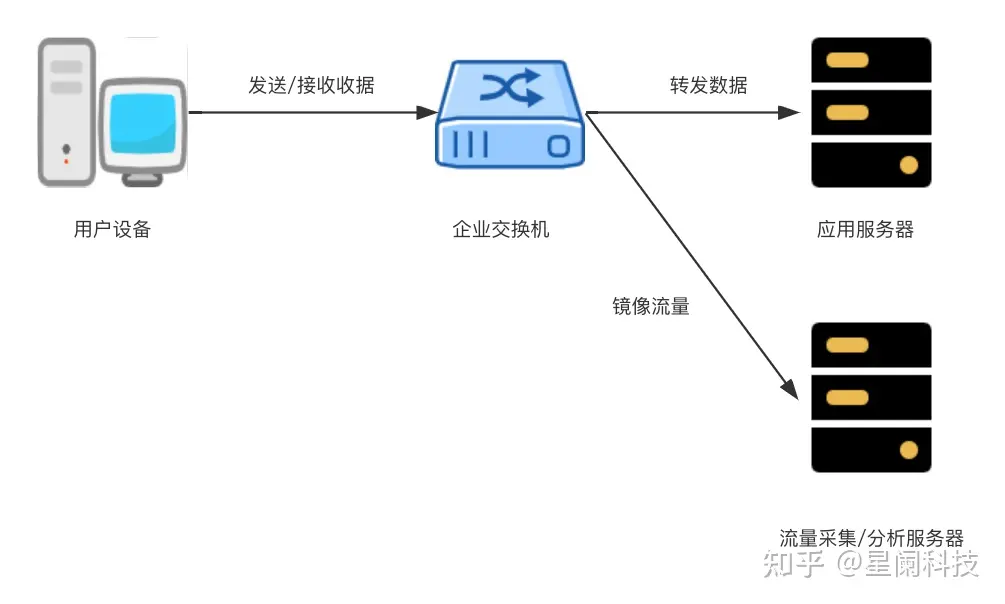
在上述架构中,交换机通过流量镜像的方式,将用户与应用服务器之间的流量“复制”给流量采集/分析服务器。流量服务器上部署的采集探针负责协议数据包的重组,以及一部分流量分析工作,比如判断数据包是否触发某些规则。此时,需要对流量采集探针进行两方面的测试工作:
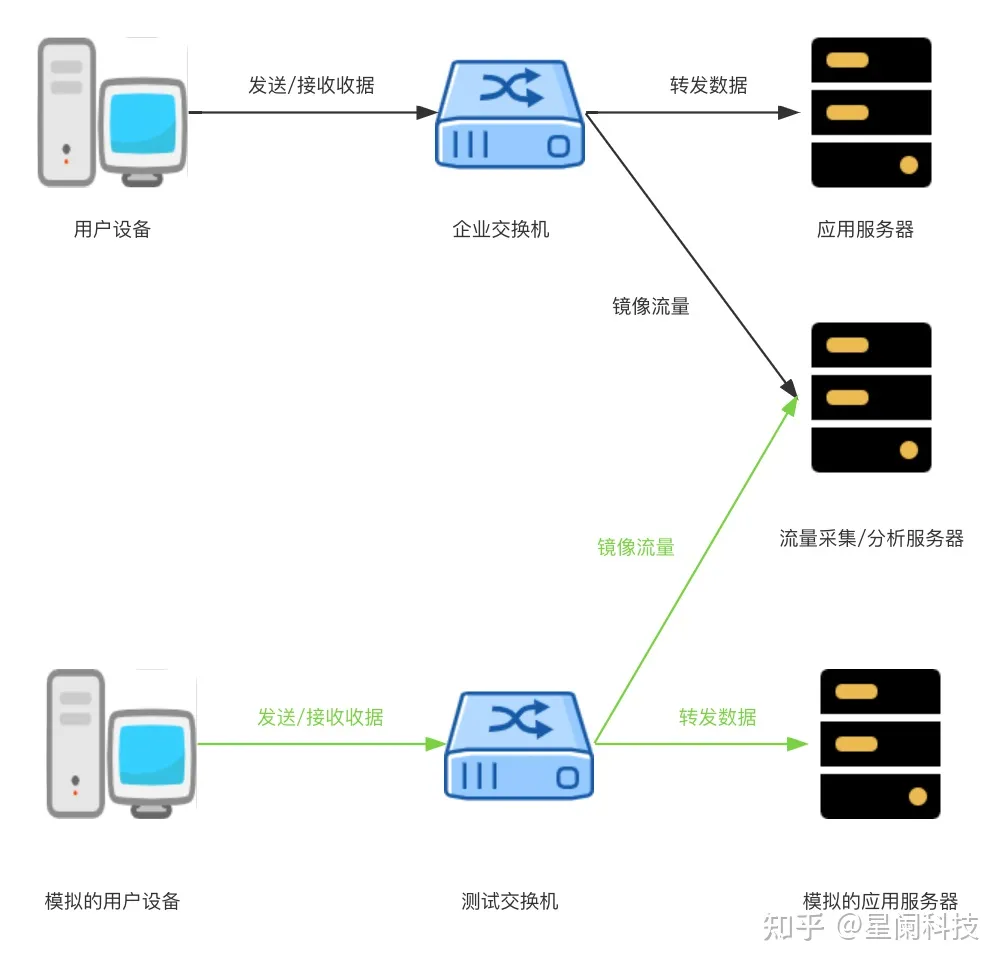
为进行性能测试,需要在模拟的用户和应用服务器之间,发送大量请求。为进行功能测试,需要在模拟的用户和应用服务器之间发送多种具有特定特征的流量。当前最主流的应用层协议非 HTTP 莫属。接下来将讲述如何使用 Lua 语言扩展 Nginx 和 Wrk,实现针对 HTTP 协议的性能测试和功能测试。
Openresty 是完全成熟的 Web 应用服务器,它捆绑了标准的 Nginx 核心,大量的第三方模块,以及它们的大部分外部依赖。
Openresty 是完全成熟的 Web 应用服务器,它捆绑了标准的 Nginx 核心,大量的第三方模块,以及它们的大部分外部依赖。
sudo yum install -y pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel perl make gcc curl zlib zlib-develwget https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.19.9.1.tar.gztar zxf openresty-1.19.9.1.tar.gzcd openresty-1.19.9.1/./configure --with-luajit --with-http_iconv_modulemake -j8 && sudo make install/usr/local/openresty/bin/openresty -Vwrk 是现代的 HTTP 基准测试工具,当在单个多核 CPU 上运行时,能够产生显著的负载。它结合多线程设计和可扩展的事件通知系统,比如 epoll 和 kqueue。
可选的 LuaJIT 脚本可以执行 HTTP 请求生成、响应处理和自定义报告。
sudo yum install -y gcc openssl openssl-devel git curlgit clone https://github.com/wg/wrk.git wrkcd wrk/ makecd wrk/ make./wrk -vWrk 支持在三个不同阶段期间执行 LuaJIT 脚本:Setup、Running 和 Done。每个 Wrk 线程拥有独立的脚本环境,Setup 和 Done 阶段在单独的环境中执行,该环境不参与 Running 阶段。
公有 Lua API 包含全局表和多个全局函数:
wrk = { scheme = "http", host = "localhost", port = nil, method = "GET", path = "/", headers = {}, body = nil, thread = , }function wrk.format(method, path, headers, body) function wrk.lookup(host, service)function wrk.connect(addr)如果能够连接到 addr,wrk.connect 返回 true,否则返回 false。addr 必须是从 wrk.lookup 返回的地址。
如下全局变量是可选的,如果定义,那么必须是函数:
function setup(thread)在已解析目标 IP 地址,并且所有线程已初始化,但尚未启动之后,Setup 阶段开始。
为每个线程,调用一次 setup(),该函数接收代表线程的 userdata 对象。
只有布尔值、nil、number 和字符串值或相同的表可以通过 get()/set() 传递,thread:stop() 只能在线程运行时调用。
function init(args)function delay()function request()function response(status, headers, body)Running 阶段从对 init() 的单次调用开始,接下来为每个请求周期调用 request() 和 response()。
init() 函数为脚本接受额外的命令行参数,必须用 “--” 将其与 wrk 参数隔开。
delay() 返回延迟发送下个请求的毫秒数。
request() 返回包含 HTTP 请求的字符串。在测试高性能服务器时,每次都构建新请求代价很大。一个方案是在 init() 中预生成所有请求,然后在 request() 中进行快速查询。
使用 HTTP 响应状态码、头和体调用 response()。解析头和体代价很大,因此如果在调用 init() 后,response 全局变量是 nil,wrk 将忽略头和体。
function done(summary, latency, requests)done() 函数接收包含结果数据,以及代表每个请求延迟和每个线程请求速率的两个统计对象的表。持续时间和延迟都是微秒值,而速率以每秒的请求数来衡量。
summary = { duration = N, -- 运行持续时间,单位为微秒 requests = N, -- 已完成的请求总数 bytes = N, -- 接收的总字节数 errors = { connect = N, -- Socket 连接错误总数 read = N, -- Socket 读取错误总数 write = N, -- Socket 写错误总数 status = N, -- 大于 399 的 HTTP 状态码总数 timeout = N -- 请求超时总数 } }图片是非常常见的资源类型,常见图片格式包括 JPG、PNG、GIF 等。测试过程中,可能希望模拟的服务端返回具有指定宽度和高度的图片。Pillow 是 Python 中强大的图片处理库,接下来使用 Pillow 生成随机的 JPG、PNG、GIF 图片。
首先,需要安装 Pillow:
pip install pillowimport stringimport typingfrom optparse import OptionParserimport randomimport osfrom PIL import Image, ImageDrawdef generate_jpg(width: int, height: int, output: str) -> None: """ 生成一张随机的 JPG 图片 :param width: 生成的图片的宽度 :param height: 生成的图片的高度 :param output: 输出文件名称 """ img: Image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height)) pixels = img.load() for x in range(width): for y in range(height): r = random.randint(0, 255) g = random.randint(0, 255) b = random.randint(0, 255) pixels[x, y] = (r, g, b) img.save(output, format="JPEG") print(f"the generated JPEG image is stored in {output}, file size is {os.stat(output).st_size / 1024} KB")def generate_png(width: int, height: int, output: str) -> None: """ 生成一张随机的 PNG 图片 :param width: 生成的图片的宽度 :param height: 生成的图片的高度 :param output: 输出文件名称 """ img: Image = Image.new("RGBA", (width, height)) draw: ImageDraw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) for x in range(width): for y in range(height): alpha = random.randint(0, 255) r = random.randint(0, 255) g = random.randint(0, 255) b = random.randint(0, 255) draw.point((x, y), fill=(r, g, b, alpha)) img.save(output, format="PNG") print(f"the generated PNG image is stored in {output}, file size is {os.stat(output).st_size / 1024} KB")def generate_gif(width: int, height: int, num_frames: int, output: str) -> None: """ 生成一张随机的 GIF 图片 :param width: 生成的图片的宽度 :param height: 生成的图片的高度 :param num_frames: 生成的图片的桢数 :param output: 输出文件名称 """ frames: typing.List[Image] = [] for _ in range(num_frames): # 生成每一帧的随机图像 image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height)) for x in range(width): for y in range(height): r = random.randint(0, 255) g = random.randint(0, 255) b = random.randint(0, 255) image.putpixel((x, y), (r, g, b)) # 将当前帧添加到帧列表中 frames.append(image) # 保存图像 frames[0].save(output, format="GIF", append_images=frames[1:], save_all=True, duration=200, loop=1) print(f"the generated GIF image is stored in {output}, file size is {os.stat(output).st_size / 1024} KB")def generate_text(size: int, output: str) -> None: """ 生成特定长度的随机文本 :param size: 生成的随机文本的长度 :param output: 输出文件名称 """ with open(output, "wb") as fd: current_size: int = size while current_size > 0: # 每次生成 4K batch: int = min(4096, current_size) fd.write("".join([random.choice(string.printable) for _ in range(batch)]).encode()) current_size -= batch print(f"the generated text is store in {output}, file size is {os.stat(output).st_size / 1024} KB")def main() -> None: parser: OptionParser = OptionParser(usage="python %prog options...") parser.add_option("-t", "--type", dest="type", default="txt", type=str, help="the type of generated file, including jpg, png, gif, txt") parser.add_option("-w", "--width", dest="width", default=200, type=int, help="the width of image, if type is image") parser.add_option("-H", "--height", dest="height", default=200, type=int, help="the height of image, if type is image") parser.add_option("-s", "--size", dest="size", default=1024, type=int, help="the size of generated file, in bytes") parser.add_option("-o", "--output", dest="output", default="a", type=str, help="output file name") parser.add_option("-n", "--num-frames", dest="num_frames", default=10, type=int, help="the frame number of generated GIF image") options, _ = parser.parse_args() _, ext = os.path.splitext(options.output) if options.type.lower() == "jpg": if ext not in [".jpg", "jpeg", ".jfif"]: options.output += ".jpg" generate_jpg(options.width, options.height, options.output) return if options.type.lower() == "png": if ext not in [".png"]: options.output += ".png" generate_png(options.width, options.height, options.output) return if options.type.lower() == "gif": if ext not in [".gif"]: options.output += ".gif" generate_gif(options.width, options.height, options.num_frames, options.output) return if options.type.lower() == "txt": if ext not in [".txt"]: options.output += ".txt" generate_text(options.size, options.output)if __name__ == "__main__": main() python3 generate_image.py -t gif -o 100x100.gif --width 100 --height 100 --num-frames 20.├── generate_image.py├── nginx.conf└── wrk.luamkdir -p static/mkdir -p logs/cp /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/mime.types .python3 generate_image.py -t gif -w 100 -H 100 -o static/100x100.gif
python3 generate_image.py -t png -w 100 -H 100 -o static/100x100.png
python3 generate_image.py -t txt -s 131072 -o static/128k.txtlocal counter = 1local threads = {}function setup(thread) thread:set("id", counter) table.insert(threads, thread) counter = counter + 1end-- 在 init 中预生成所有请求,在 request 中顺序选择function init(args) current_index = 0 -- 保存所有预生成请求的表 pregenerated_requests = {} table.insert( pregenerated_requests, wrk.format( "GET", "/path/1", { ["X-Predefined-Strategy"] = "png,100x100.png" } ) ) table.insert( pregenerated_requests, wrk.format( "POST", "/path/2", { ["X-Predefined-Strategy"] = "gif,100x100.gif", ["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, "foo=bar&baz=quux" ) ) table.insert( pregenerated_requests, wrk.format( "PUT", "/path/3/arbitrary/here", { ["X-Predefined-Strategy"] = "text,128k.txt", ["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, "foo=bar&baz=quux" ) ) table.insert( pregenerated_requests, wrk.format( "GET", "/path/4", { ["Content-Type"] = "application/json;charset=utf8" }, [[ { "headers": {"x-header-a": "a", "content-type": "text/plain"}, "status_code": 200, "body": "this is a very very simple text body, but it maybe meet some rules." } ]] ) )endfunction request() current_index = current_index + 1 return pregenerated_requests[current_index%#pregenerated_requests+1]end worker_processes auto;error_log logs/error.log;error_log logs/error.log notice;error_log logs/error.log info;pid logs/nginx.pid;events { worker_connections 4096;}http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 15; open_file_cache max=2048 inactive=30s; open_file_cache_valid 10s; open_file_cache_min_uses 1; open_file_cache_errors on # 请求体不能超过该设置。 # 如果客户端需要传递更大的请求体,那么调整该设置 client_max_body_size 10m; # 预置策略。 # 预置策略通过名称进行唯一标识。 # 预置策略封装响应码、响应头和响应体(可选),可避免客户端重复传输这些内容。 # 客户端通过请求头指定使用的策略。 # 如此一来,客户端可以同时自由地定制请求和响应,只多出用于指定所用策略的请求头。 # 服务端使用紧跟在策略名称后面的磁盘文件名称,获取响应体。 # 因此,需要提前将生成的响应体存储到磁盘文件。 # 如果未提供文件名称,并且策略中存在响应体,那么使用策略中的响应体。 # 如果都未提供,那么返回空响应体。 # 请求头类似 X-Predefined-Strategy: png,100x100.png 或 X-Predefined-Strategy: forbidden。 # 注意: # 1. 预置的响应体不能太大,否则将占用太多的共享内存 # 2. 预置策略名称不能包含 "," # 3. 预置策略中指定的响应头名称不会被规范化,因此设置时,需要注意 lua_shared_dict predefined_stategies 128m; init_by_lua_block { -- 保存策略 local function save_strategy(name, status_code, headers, body) if name == nil then return ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "no strategy name provided") end local t = { status_code = status_code or ngx.HTTP_OK, headers = {}, body = body or "" } for name, value in pairs(headers or {}) do t.headers[name] = value end local cjson = require("cjson.safe") local j = cjson.encode(t) if j == nil then return end local s = ngx.shared.predefined_stategies local suc, err = s:set(name, j) if suc then ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "setting strategy " .. name .. " succeeded") else ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "setting strategy " .. name .. " failed with " .. err) end end -- 按需添加策略 save_strategy("png", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="image/png"}) save_strategy("jpeg", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="image/jpeg"}) save_strategy("gif", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="image/gif"}) save_strategy("ico", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="image/x-icon"}) save_strategy("text", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="text/plain"}) save_strategy("json", ngx.HTTP_OK, {["Content-Type"]="application/json;charset=utf8"}) save_strategy( "forbidden_default", ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN, {["Content-Type"]="text/plain"}, "forbidden" ) save_strategy( "notfound_default", ngx.HTTP_NOT_FOUND, {["Content-Type"]="text/plain"}, "not found" ) } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location /static { alias static/; } location / { content_by_lua_block { local cjson = require "cjson.safe" -- 规范化响应名称 local normalize_header = function(name) -- 1. _ 替换成 - name = string.gsub(name, "_", "-") -- 2. 第一个字符大写 name = string.gsub(name, "%w", function(m) return string.upper(m) end, 1) -- 3. - 后面的字符大写 return string.gsub(name, "-%w", function(m) return string.upper(m) end) end -- 生成指定长度的随机字符串 local function generate_random_string(length) local chars = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789" -- 使用当前时间作为随机种子 math.randomseed(os.time()) local r = "" for _ = 1, length do local idx = math.random(1, #chars) r = r .. string.sub(chars, idx, idx) end return r end -- 当指定的策略或路径不存在时,返回该响应码 local strategy_not_found_status = ngx.HTTP_NOT_FOUND local strategy local path local predefined_strategy_hdr = ngx.var.http_x_predefined_strategy -- 如果客户端指定策略 if predefined_strategy_hdr ~= nil then local start_pos, end_pos = string.find(predefined_strategy_hdr, ",", 1, true) if start_pos == nil then strategy = predefined_strategy_hdr else strategy = string.sub(predefined_strategy_hdr, 1, start_pos-1) path = string.sub(predefined_strategy_hdr, end_pos+1) end -- 获取策略 local s = ngx.shared.predefined_stategies strategy = s:get(strategy) -- 如果策略不存在,那么返回错误 if strategy == nil then ngx.status = strategy_not_found_status ngx.header.content_type = "text/plain" ngx.say("the provided stategy not found") return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) end -- 根据策略设置响应 strategy = cjson.decode(strategy) ngx.status = strategy.status_code for name, value in pairs(strategy.headers or {}) do ngx.header[name] = value end -- 设置响应体 if path == nil then ngx.print(strategy.body) return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) end -- 发起子请求,从磁盘获取响应体 local res = ngx.location.capture("/static".."/"..path) if res.status == ngx.HTTP_OK then ngx.print(res.body) else ngx.status = strategy_not_found_status ngx.header.content_type = "text/plain" ngx.say("the provided path not found") end return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) end -- 非策略模式用于构建期望的响应 -- 当请求体不合法时,返回该响应码 local bad_request_status_code = ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUEST -- 读取请求体 ngx.req.read_body() local body_raw = ngx.req.get_body_data() -- 解析请求体 local body, err = cjson.decode(body_raw) -- 解析请求体失败 if err ~= nil then ngx.status = bad_request_status_code ngx.say(err) return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) end -- 设置响应码 local status_code = body["status_code"] if status_code == nil then status_code = ngx.HTTP_OK end ngx.status = status_code -- 设置响应头 for name, value in pairs(body["headers"] or {}) do ngx.header[normalize_header(name)] = value end -- 设置响应体 if body["body"] then -- 使用客户端指定的响应体 ngx.print(body["body"]) else -- 使用客户端指定的随机响应体长度生成响应体。 -- 指定的长度越长,生成随机字符串的效率越低,请设置合理的长度 if body["random_body_length"] then ngx.print(generate_random_string(tonumber(body["random_body_length"]))) else -- 返回空响应体 ngx.print("") end end return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) } } }}关于 generate_image.py 的内容,请参阅前一章节。
/usr/local/openresty/bin/openresty -p . -c nginx.confcurl \
-w 'url effective: %{url_effective}\nhttp code:%{http_code}\ntime total: %{time_total}\ntime namelookup: %{time_namelookup}\ntime connect: %{time_connect}\ntime appconnect: %{time_appconnect}\ntime pretransfer: %{time_pretransfer}\ntime redirect: %{time_redirect}\ntime starttransfer: %{time_starttransfer}\nsize download: %{size_download}\nsize request: %{size_request}\n' \
-X POST \
-H "content-type: application/json" \
-d '{"headers": {"x-header-a": "a", "x-header_b": "b"}, "status_code": 200, "random_body_length": "65536"}' \
-v -o /dev/null \
http://127.0.0.1/pathWrk 的命令行选项如下:
使用如下命令进行测试:
wrk -s wrk.lua --latency -t 16 -c 1600 -d 300s http://127.0.0.1"GET /path/1 HTTP/1.1" 200 40181
"POST /path/2 HTTP/1.1" 200 141424
"PUT /path/3/arbitrary/here HTTP/1.1" 200 131086
"GET /path/4 HTTP/1.1" 200 78Running 5m test @ http://127.0.0.1
16 threads and 1600 connections
Thread Stats Avg Stdev Max +/- Stdev
Latency 18.22ms 27.01ms 1.84s 94.58%
Req/Sec 6.00k 0.96k 16.17k 72.14%
Latency Distribution
50% 11.36ms
75% 19.14ms
90% 30.21ms
99% 133.45ms
28642285 requests in 5.00m, 2.04TB read
Requests/sec: 95443.39
Transfer/sec: 6.97GB地址:北京市海淀区海淀大街38号银科大厦6层
Copyright © 2022 北京星阑科技有限公司. 京ICP备19053406号
提交成功